Radiobiology
What is radiobiology?
Radiobiology is the study of the action of ionizing radiation on living organisms. It seeks to answer questions such as: How can we tell if someone or something been exposed to radiation? What happens to the organism if it has been exposed? What can be done to mitigate the effects, if any?
Biological effects of radiation exposure can be studied at three levels – molecular, cellular and physiological. Molecular and cellular effects can be observed in minutes to days after exposure, and are useful tools to target for medical intervention after radiation exposure. Physiological effects occur over an organism’s lifetime; studying them can give a holistic understanding of biological effects.

Attribution: Figures composed from individual subunits provided in Servier Medical Art by Servier, under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License
Our objectives:
The goal of radiobiology research in SNRSI is to understand the effects of radiation, especially long term and/or low dose rate exposure. There is an ongoing global discourse on the consequences of such exposure, and we aim to contribute to this discourse by focusing on how this impacts our Singapore population, based on our unique ethnic and geographical landscape. Through our research, we hope to be able to explore the relevance of appropriate exposure threshold limits, and in the long term, evaluate if measures to reduce the effects exposure are necessary.
Our facilities:
Chronic low dose rate irradiator

A low dose rate Cesium-137 source is housed within a typical cell culture incubator to facilitate the irradiation of cell and organ cultures at low doses and low dose rates.
High and low dose rate x-ray irradiator
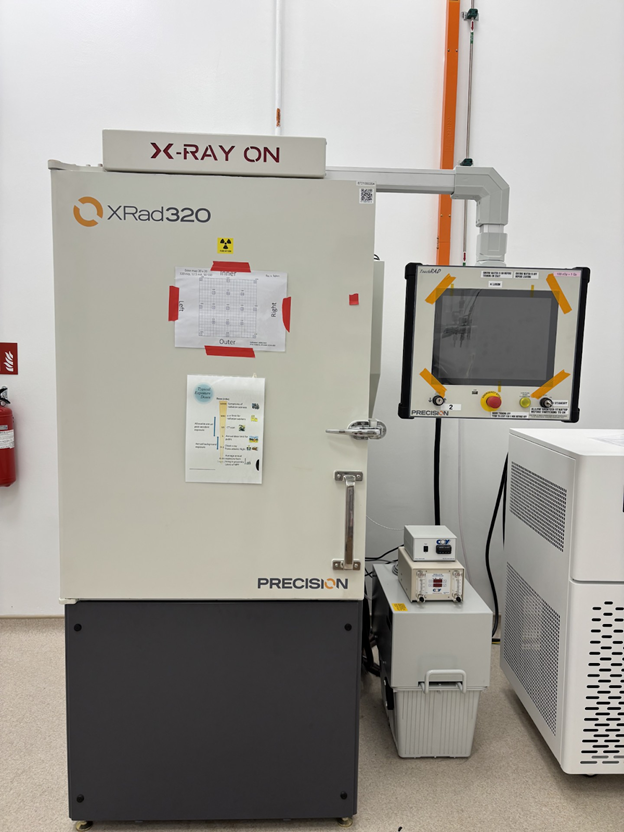

The x-ray irradiator facilitates irradiation of samples at a range of dose rates, to enable the study of differences in radiobiological response to high vs low dose rates.
G10 Gamma Irradiator for chronic low-dose rate irradiation of animals
Automated detection and scoring system for cytogenetic assays

This setup enables the automatic scanning of chromosomal aberrations to standardize and streamline the processes involved in techniques for biodosimetry (the association of biological observations with radiation dose received).
Stereologer System

This setup provides meaningful quantitative descriptions of the geometry of 3D structures from measurements that are made on 2D images, to enable the study of physiological responses in various tissues and organs.
FLUOVIEW FV3000 series of confocal laser scanning microscopes

This confocal microscope enables a wide range of imaging modalities, including macro-to-micro imaging, super resolution microscopy, and quantitative data analysis.
ZEISS Axio Zoom.V16 with ApoTome 2

Zeiss Axio Zoom. V16 Fluorescence Microscope boasts extreme brightness and high numerical aperture. Coupled to ApoTome 2 based structural-illumination insert, the system allows to view large samples, for example, the complete zebrafish in fluorescence contrast.
Zeiss Lightsheet 7 fluorescence microscope
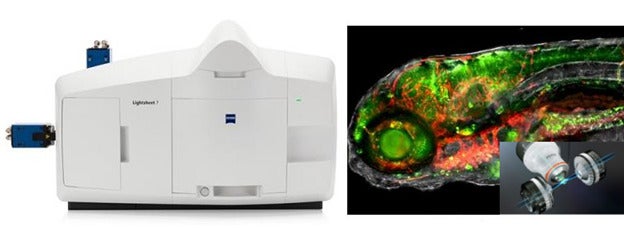
Zeiss Lightsheet 7 fluorescence microscope enables fast and gentle imaging of whole living organisms over extended periods of time. With dedicated optics, imaging chamber and in-house developed holders, we use this system to image real-time dynamics of radiation consequences in zebrafish under natural physiology.

